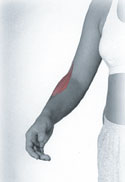
Brachioradialis
Above is the pain pattern for the Brachioradialis muscle. The pain typically begins in the thumb side of the elbow and spreads to the wrist and hand.
Activities Which Aggravate the Pain
Opening jars, using a screwdriver, hammering, tennis, racquetball, holding a coffee cup, turning doorknobs, pouring from a container, shaking hands. Positions that aggravate pain from this muscle.
Positions that Aggravate Pain from this Muscle
Holding a coffee cup or container. This figure shows where the muscle is located in the body and how it is attached to the bones of the body.
Anatomy Facts - Brachioradialis
Muscle Action
Elbow flexion in mid-position between pronation and supination.
Muscle Origin
The brachioradialis arises from the humerus above the elbow.
Muscle Insertion
This muscle inserts on the lateral side of the base of styloid process.
Muscle Innervation
The radial nerve.
Trigger Point Locations - Brachioradialis
You can find your own trigger points by using your thumb or finger to press on the spots shown in the picture. They are not difficult to find. Or you can ask a friend or family member to help you. Press firmly in a step-by-step manner until you find the exact spot that is tender. That is the trigger point.
By pressing firmly on the trigger point, and holding that pressure for several seconds, you will discover the pain lessens dramatically. In fact there are devices that can help you do this. We recommend a device called a "TheraCane" that can be purchased at many stores such as Sammons Preston Medical Equipment that has a mail order catalogue that can be contacted at 1 800 323-5547. The TheraCane is their item # 5244. The TheraCane can use be purchased at many local pharmacies.
Unfortunately this technique, known as acupressure, or shiatsu, provides only temporary relief. Some physicians inject drugs like Novocaine into trigger points, but these offer only temporary relief as well, and can cause scar tissue in the muscle.
Isometric Contraction Testing - Brachioradialis
A painful muscle will become more painful if it is forcefully contracted (flexed). Use this picture to test this for yourself with the assistance of a friend or family member.
Follow these Directions
Sit with a pillow on your lap. Place your painful forearm on the top of the pillow with your thumb facing upwards. Place your opposite hand on top of the painful forearm. Try to lift the thumb toward your face by bending at the elbow while resisting this movement with your other hand on the forearm.